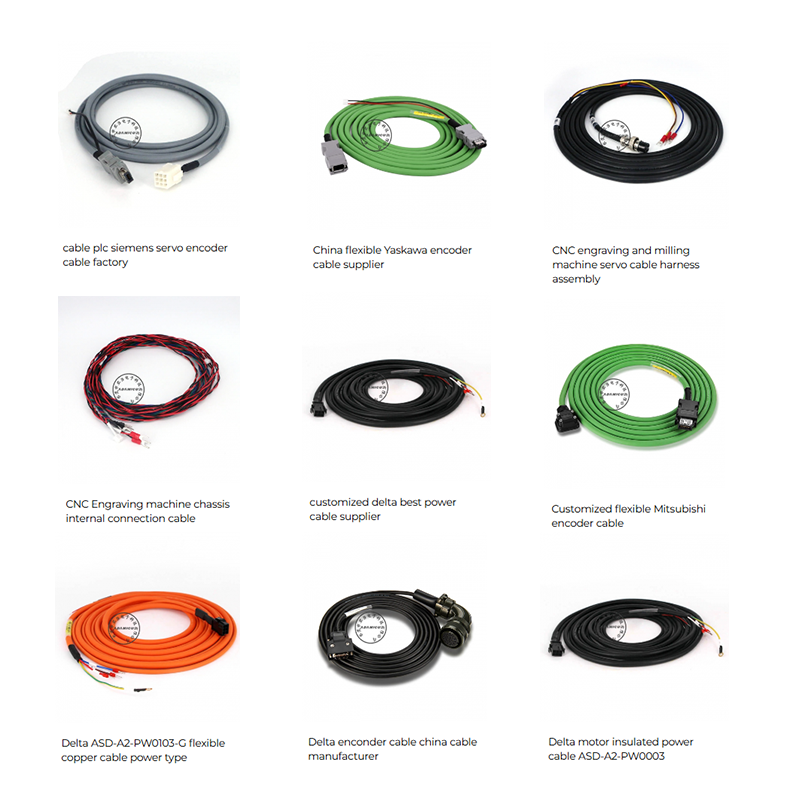
Servo motor cables are special cables used to connect servo motors with devices such as controllers or frequency converters to achieve power transmission and signal control. Here are some important information about servo motor cables:
1. Cable structure:
• Conductor: Usually composed of multiple strands of finely twisted tinned copper wires. This design not only ensures good conductivity, but also has a certain degree of flexibility and can withstand frequent bending and movement. Too thick copper wires will affect the bending life of the cable, and too thin copper wires may cause entanglement.
• Insulation: Special hard heat-resistant and flame-retardant materials such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and TPE (thermoplastic elastomer) are used, which have good insulation properties. At the same time, the non-adhesiveness and anti-aging properties of the insulation layer should be considered to ensure the safety and reliability of the cable during long-term use.
• Filling: In the cabling process, different fillers are used to ensure that the core wires of the cable will not be dislocated or deformed during movement and bending. The center filling increases the support of the cable twisting process, and the filling of the core cross area ensures the roundness of the cable molding.
• Shielding layer: Generally, the structure of shielding tinned copper mesh wrapped with aluminum foil is adopted, and a layer of tinned copper mesh is woven as a whole. The density of the braided layer needs to be reasonably controlled. If it is too loose, the shielding effect cannot be achieved, and if it is too tight, it will affect the use effect of the cable. Good shielding performance can effectively resist external electromagnetic interference and ensure the accuracy of signal transmission.
• Outer sheath: The sheath material is diverse, and the common ones are PVC, NBR (nitrile rubber), PUR (polyurethane), etc. According to the specific use environment, such as oily environment, low temperature environment, water environment, acid and alkali corrosion environment, etc., select the corresponding sheath material.
2. Cable type:
• Power structure cable: Mainly used to transmit electrical energy and provide power for servo motors. Usually composed of 4 cores, generally including three-phase power cord and a ground wire. This cable can withstand large currents and has a higher voltage level to meet the power requirements of servo motors.
• Power + control structure cable: In addition to transmitting power, it also contains one or more pairs of control lines for transmitting control signals, such as feedback signals such as the position, speed, torque, etc. of the servo motor and command signals issued by the controller. This type of cable is more complex in structure and needs to ensure the stability and accuracy of power transmission and signal transmission at the same time.
3. Performance characteristics:
• High flexibility: It can withstand frequent mechanical stresses such as bending, stretching, and torsion, and is suitable for the connection needs of servo motors in various motion scenarios, such as joint movement of robots, conveying devices of automated production lines, etc.
• Heat-resistant and flame-retardant: During operation, the servo motor and its connecting cable may generate heat, so the cable needs to have good heat resistance and be able to work normally under certain high temperature environments. At the same time, the flame-retardant property can prevent the spread of fire in the event of an accident such as a fire, thereby improving the safety of the system.
• Anti-interference: Since the servo system has very high requirements for the accuracy and stability of the signal, the servo motor cable needs to have good anti-interference performance, which can effectively resist the interference of external electromagnetic signals and ensure the quality of signal transmission.
• Wear resistance: In some harsh working environments, such as those with friction and wear, the outer sheath of the cable needs to have high wear resistance to extend the service life of the cable.
4. Application scenarios: Widely used in CNC machine tools, robots, automated production lines, medical equipment, electronic equipment and other mechanical equipment that require precise control and movement.