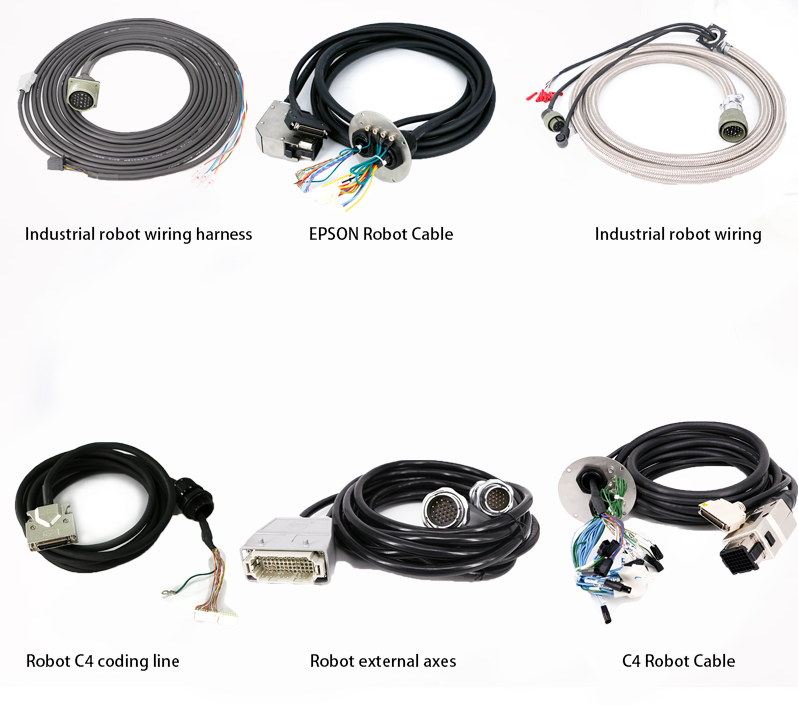
Robot cable refers to the robot body, power supply, signal, control and robot peripheral wires. Here are some detailed information about robot cables:
1. Performance characteristics:
• Flexibility: Industrial robot equipment often completes grabbing, handling and other actions through the bending of joint nodes, so the cable needs to have high flexibility and bending resistance to be suitable for occasions where bending stress exists for a long time.
• Torsion resistance: As the number of joints of robot equipment increases and the flexibility of the arm increases, the cable must meet the torsion requirements of equipment operation, not easily damaged during the torsion process, and ensure the stability of signal and power transmission.
• Functionality: It can be customized as a composite cable according to needs, and it can also undertake multiple functions such as control, signal transmission and power connection.
• Environmental adaptability: Robots are often used in complex and harsh environments, such as wear, oil, water, corrosive substances, etc., so the cable has high requirements for wear resistance, oil resistance, waterproof, corrosion resistance, and aging resistance.
2. Structural composition:
• Conductor structure: Generally composed of multiple strands of finely twisted copper wires to ensure good conductivity and flexibility, usually in accordance with relevant international electrical standards (such as IEC 60228).
• Core wire insulation: Use highly flexible insulating materials such as polyurethane, nitrile rubber, etc. to ensure that it will not break or lose insulation during the movement of the robot.
• Tensile element: There are sufficient tensile fibers in the cable core to enhance the tensile strength of the cable so that the cable can withstand tension during the repeated movement of the robot.
• Stranded wire structure: The structural design and pitch of the stranded wire need to be accurately calculated and optimized to ensure the flexibility and signal transmission performance of the cable.
• Inner sheath: It plays a role in protecting the cable core and can also increase the overall strength and wear resistance of the cable.
• Shielding braid: Usually tinned copper braiding is used, and the coverage rate is generally around 85%, which can reduce the interference of external electromagnetic signals on the internal signals of the cable and ensure the accuracy of signal transmission.
• Outer sheath: The materials of the outer sheath are generally PVC (polyvinyl chloride), TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer rubber), PUR (polyurethane), etc., which have the characteristics of wear resistance, oil resistance, low temperature resistance, hydrolysis resistance, etc., and can adapt to different working environments.
3. Application fields:
• Industrial automation: Applicable to industrial robots, automated machine tools and other equipment, such as welding robots, assembly robots, handling robots, spraying robots, etc., to meet the requirements of these equipment for bending resistance, torsion resistance, and sliding resistance.
• Automobile production: Used in automobile production lines, including power supply and signal transmission of robots and automated equipment in the installation, welding, and painting of automobile parts.
• Logistics handling: In logistics handling equipment, such as automatic guided vehicles (AGVs), palletizing robots, etc., robot cables provide power and control signals for the normal operation of the equipment.
• Other fields: It can also be used in robots or automated equipment in special environments such as construction engineering, cranes, excavators, and underwater detection projects.