I am a machine vision engineer. My friends often ask me, “What exactly does machine vision do?” After I explain it to them, they seem to understand it, and it is indeed a difficult concept for people outside the industry to understand.
My customers often ask me, “What can machine vision do? What is the principle of detection?” After I popularized some industry knowledge to my customers, our cooperation and communication became smooth and pleasant.
So I want to write an article to let more people understand what machine vision is, why we use machine vision, what problems machine vision can solve, and in what fields it can be applied. With these questions, let’s explore “machine vision” with me.
What is machine vision? It sounds very high-sounding. In simple terms, it is to use machines to replace human eyes for measurement and detection. Machine vision is a branch of artificial intelligence and is a comprehensive technology that requires the combination of software and hardware.
Machine vision is not an independent thing, but a system that requires multiple components to work together, so the “machine vision” we often say is actually a “machine vision system”. The machine vision system consists of a camera, lens, light source, image processing software, cables and communication interfaces.
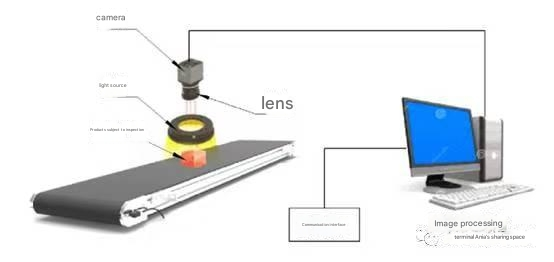
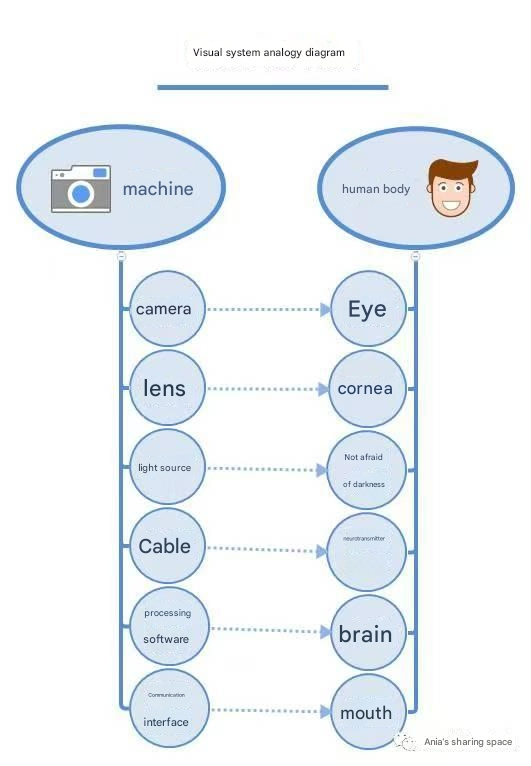
The principles of the machine vision system are similar to those of the human vision system. If you think about how we use our eyes to detect the quality of a product, it is easy to remember the composition and principles of the machine vision system. If you compare the camera to an eye, the camera lens is the cornea that provides refractive power, the image sensor in the camera is the retina that senses light and forms an image, the light source provides a stable lighting environment (so you don’t have to worry about darkness), the communication cable is the neurotransmitter that transmits information, the image processing software is the brain that processes information and makes judgments, and the communication interface is the mouth that speaks the results.
Why use machine vision?
If you have been to a manufacturing workshop or worked there, you will find that the operators do simple and repetitive work every day, sometimes even repeating the same action thousands of times, which is anti-human! So even if the salary is getting higher and higher, fewer and fewer people are willing to do such work, and they often leave after working for a few months. This is undoubtedly a huge problem for the factory. As the saying goes, every profession has its own specialty, and such simple and repetitive work is best done by machines, so machine vision came into being.
What are the advantages of machine vision compared to humans?
First of all, once machine vision is debugged and developed, it can start working immediately, without slacking off due to fatigue, and can even run continuously for 24 hours, all year round. It does not rely on experience and responsibility, and is more efficient and more stable.
Secondly, machine vision systems often establish data links with other devices, and all data can be recorded and saved, which is convenient for data analysis and process optimization, providing extremely high additional production capacity.
Finally, special environments such as extremely high temperatures, extremely high dust, and the release of toxic gases are not suitable for people to work. Machine vision products are waterproof and dustproof, which can help us complete those dangerous tasks.
Leave simple and repetitive work to machines and free your hands to do more creative things. Intelligent production with machines replacing people is the general trend. Germany has proposed Industry 4.0, and China has also made a grand plan to realize intelligent manufacturing by 2025, and machine vision is an important part of it.
What problems can machine vision solve?
Machine vision can mainly solve four types of problems: detection, measurement, guidance, and recognition.
1
Inspection
Inspect products, such as whether there are any errors or omissions in the production process, defective product inspection, package counting, etc.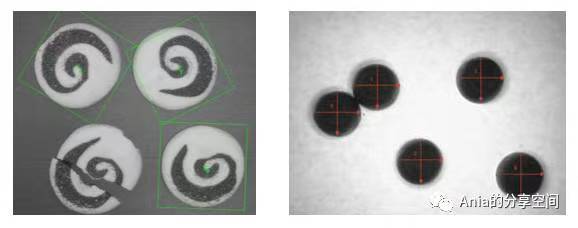
2
Measurement
Measure the product’s angle, arc, radius, length, width, distance, etc.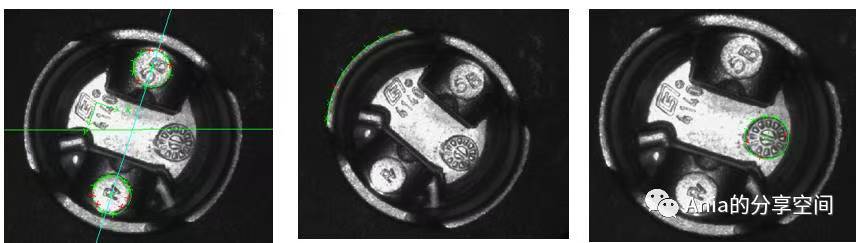 3
3
Guidance
Guide the robot arm, guide the robot arm to grasp, weld, dispense glue, lock screws, etc. through visual positioning. 4
4
Identification
Identify barcodes and QR codes, identify characters, and thus trace products.
Application fields of machine vision
In what fields can machine vision be applied?
The answer is almost all!!!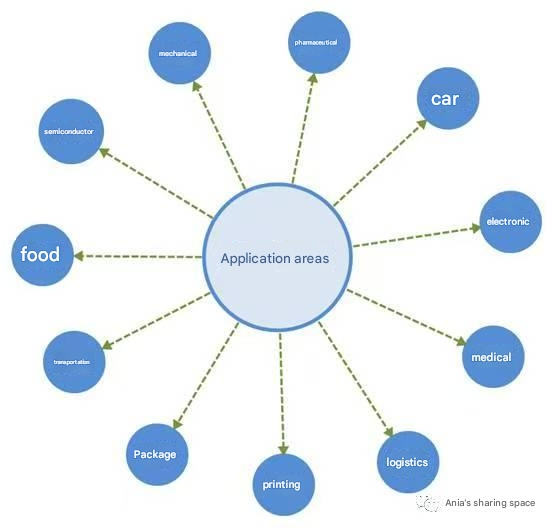
Is machine vision really that powerful? Don’t disbelieve it~ The mobile phone you are looking at right now has many machine vision applications in the production process. Each part must be measured by machine vision to ensure the size is qualified. The QR code barcode on the part also needs machine vision to identify and trace. The robot is guided by machine vision to accurately install each part. After the installation is completed, the machine vision also detects whether the part is installed in place. Of course, this is just a simple process description. In fact, the birth of a product is a result of many complex processes and the cooperation of various equipment.
Machine vision is not only in factories, but also in our lives. The automatic license plate recognition system in the parking lot and the barcode scanning at the checkout in the supermarket are all applications of machine vision. It is not far away at all, but right next to you.
–