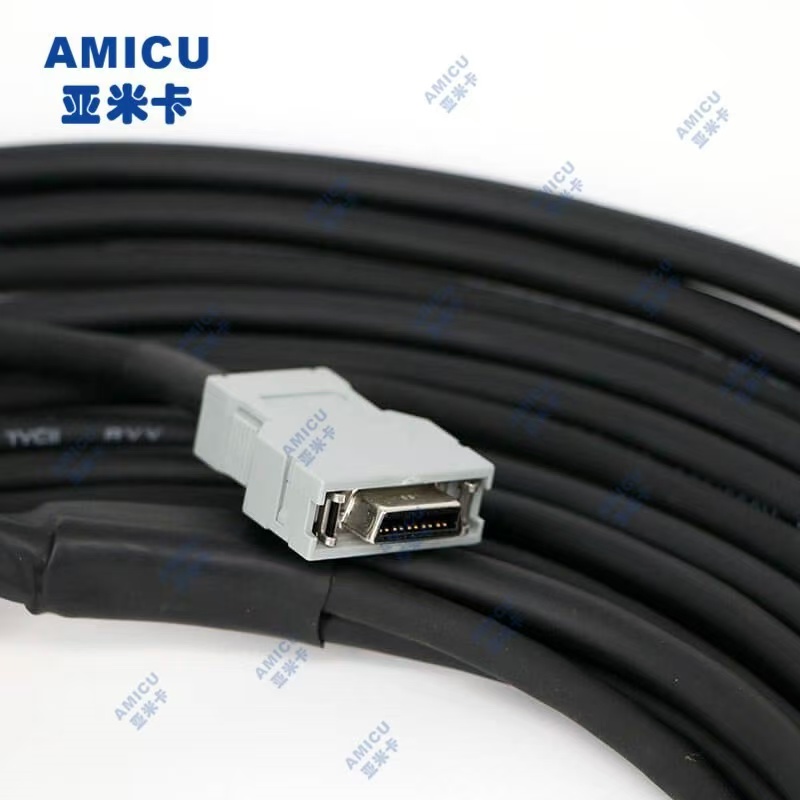
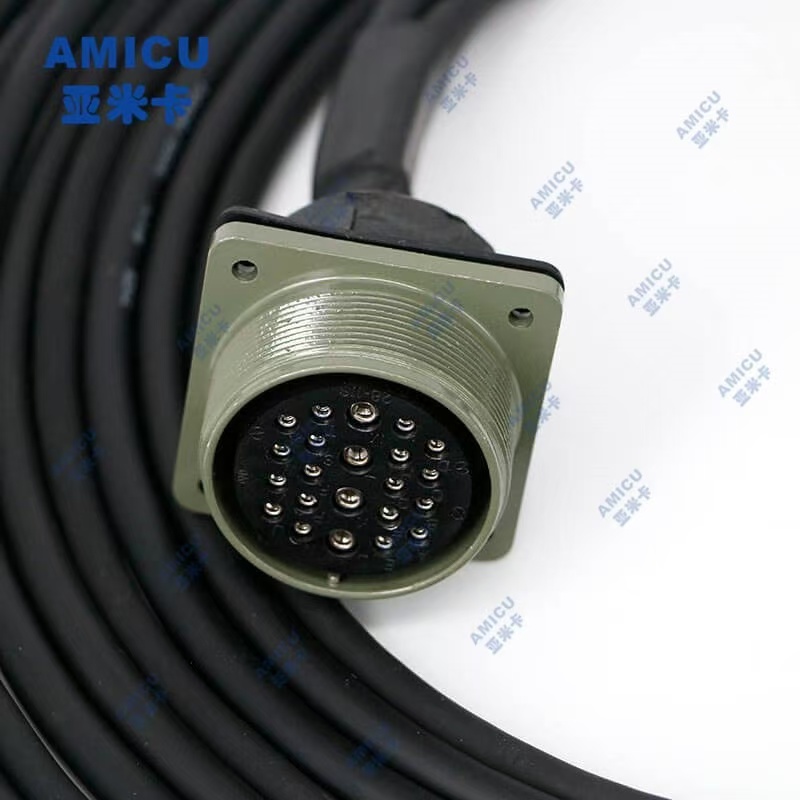
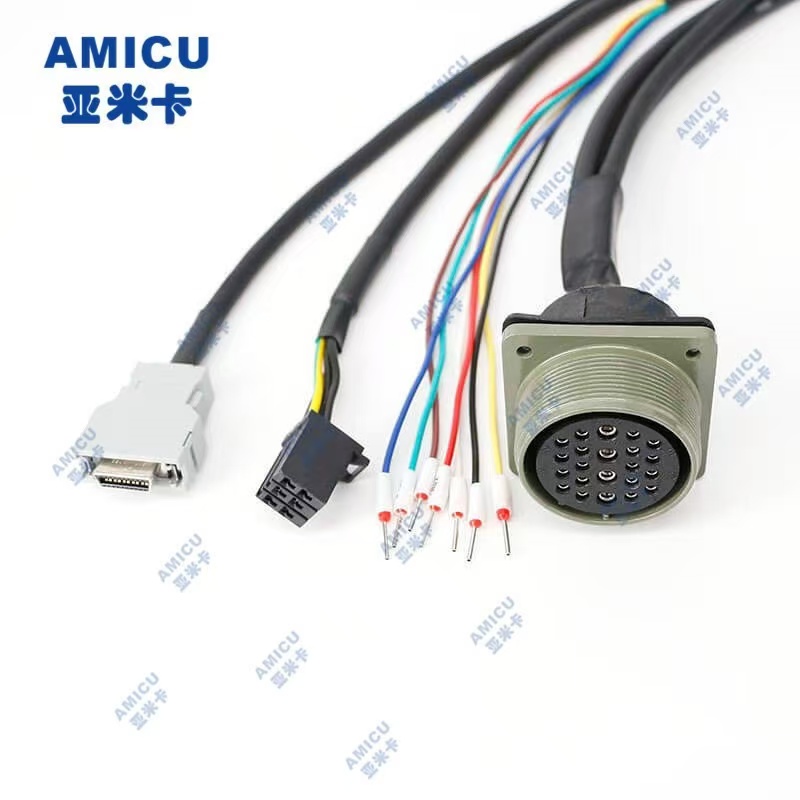
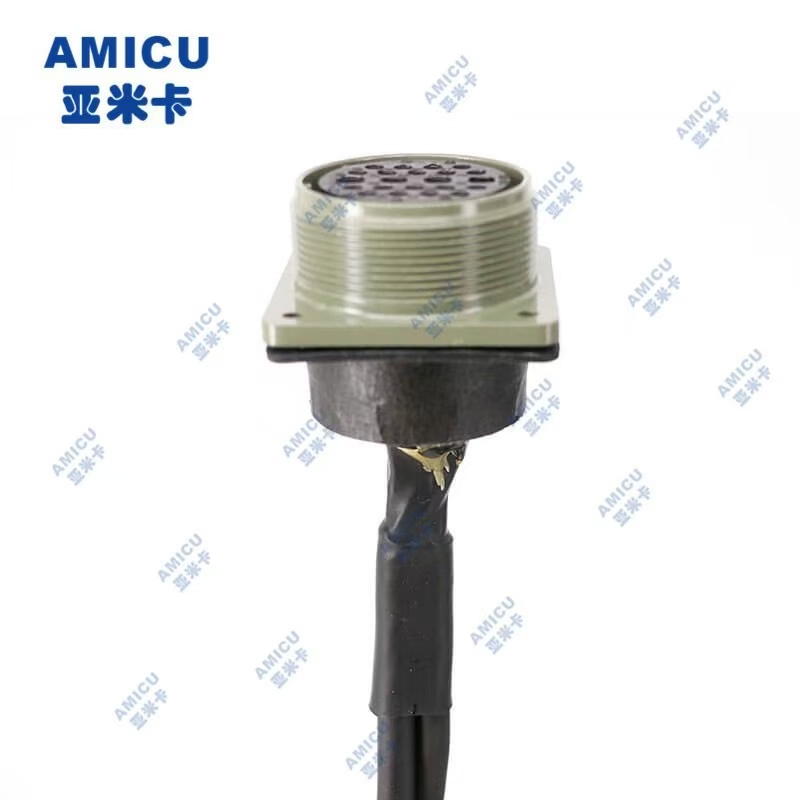
Industrial robot harness is a wire and cable assembly that connects industrial robots with external devices, power supplies, sensors, controllers and other components. It is one of the key components for the normal operation of industrial robots. Here are some detailed information about industrial robot harnesses:
1. Components:
• Wire: It is the core part of the harness and is used to transmit power and signals. It is generally made of metal materials with good conductivity such as copper, and the cross-sectional area and wire diameter of the wire will vary according to different current and signal transmission requirements.
• Connector: It is used to connect the wires and various components of the robot to ensure the stable transmission of signals and power. There are many types of connectors, including plugs, sockets, terminals, etc., which need to be selected according to the specific interface type and connection requirements of the robot.
• Insulation layer: It is wrapped around the outside of the wire to play an insulating and protective role to prevent faults such as short circuits between wires or between wires and the outside world. The material of the insulation layer usually has good insulation performance, high temperature resistance and wear resistance, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE), polyurethane (PUR), etc.
• Sheath: It is wrapped around the outside of the wire and connector to play a protective and fixed role. The material of the sheath needs to have good wear resistance, bending resistance, tensile resistance and aging resistance to adapt to the complex working environment of industrial robots.
2. Performance requirements:
• Strong signal transmission capability: The work of industrial robots requires precise control and real-time signal transmission, so the wiring harness must be able to accurately and quickly transmit various signals, such as control signals, sensor signals, feedback signals, etc. This requires the wiring harness to have low resistance, capacitance and inductance, as well as good shielding performance to reduce signal interference and attenuation.
• Good wear resistance: During the operation of industrial robots, the wiring harness will often be subjected to mechanical stress such as friction, pulling and bending, so it must have good wear resistance and bending resistance to ensure the service life of the wiring harness.
• Good high and low temperature resistance: Industrial robots may work in different temperature environments, so the wiring harness must be able to maintain good performance in high and low temperature environments, such as high temperature resistance, low temperature resistance, cold and heat shock resistance, etc.
• Good waterproof and dustproof performance: In some harsh working environments, such as humid, dusty, oily and other environments, the wiring harness must have good waterproof and dustproof performance to prevent moisture and dust from entering the wiring harness and affecting signal transmission and electrical performance.
3. Types and application scenarios:
• Robot body wiring harness: mainly connects the various joints, motors, sensors and other components of the robot to provide power and signal transmission for the robot body. For example, the wiring harness used to connect the robot’s joint drive and controller needs to be able to withstand frequent bending and stretching movements.
• Control cabinet wiring harness: connects the robot’s control cabinet and other external devices, such as power supplies, programmers, displays, etc. The control cabinet wiring harness usually needs to have a high signal transmission rate and stability to ensure the normal operation of the robot’s control and monitoring system.
• End effector wiring harness: connects the robot’s end effector, such as fixtures, spray guns, welding heads, etc., to provide power and control signals for the end effector. The end effector wiring harness needs to be customized according to different end effector types and working requirements to meet their special connection and signal transmission needs.
4. Manufacturing process:
• Wire cutting: According to the design requirements of the wire harness, the wire is cut into the required length. The precision and quality of wire cutting directly affect the connection performance and reliability of the wire harness.
• Stripping: Strip the insulation layer at both ends of the wire to a certain length to expose the metal part of the wire for crimping or welding of the connector. The length and quality of the stripping need to be strictly controlled to ensure good contact between the wire and the connector.
• Crimping or welding: Connecting the connector to the wire can be done by crimping or welding. Crimping is a commonly used connection method with the advantages of reliable connection, simple operation and high efficiency; welding is suitable for some occasions with high requirements for connection strength and stability.
• Assembly and testing: Assemble the connected wires and connectors to form a complete wire harness. After assembly, the wire harness needs to be strictly tested, including conduction test, insulation test, voltage resistance test, etc., to ensure that the performance and quality of the wire harness meet the requirements.